Key points about accuracy in maths

give a range of values that a (to) roundIn the context of a number, express to a required degree of accuracy, eg 543 rounded to the nearest 10 is 540. number could have.
Use the inequality symbols (< >)The symbol > is used when a value is greater than another, eg 23 > 5. The symbol < is used when a value is less than another, eg 11 < 40. less than or equal to (≤) and less than (<) when writing limits of accuracy, to show the and upper boundThe greatest value. bounds.
Work out limits more easily by recognising the degree of accuracyDescribes how a value has been approximated, for example, to a number of decimal places (d.p.) or significant figures (s.f.). to which a value has been rounded, such as decimal places or significant figures, sometimes by .
Refresh your knowledge with these guides on rounding decimals and rounding to significant figures.
What are limits of accuracy?
To find the limits of accuracy when a number has been rounded:
Identify the degree of accuracy to which a number has been rounded in terms of place valueThe value of a digit that relates to its position or place in a number, eg in 1482 the digits represent 1 thousand, 4 hundreds, 8 tens and 2 ones., nearest ten, nearest integerIntegers are numbers with no fraction or decimal part. They can be positive, negative or zero. 42, –8, and 10,000 are examples of integers., nearest tenth etc.
Divide the degree of accuracy by two (ie halve it):
Add to the number for the upper limit, the maximum.
Subtract from the number for the lower limit, the minimum.
To find the limits for a number:
Upper limit:
Increase the final digit of a decimal number by 1.
Increase the last non-zero digit of a whole number by 1.
Lower limit:
- Use the number itself.
The error interval is written as lower limit ≤ number < upper limit.
The number can take any value from the lower limit, up to but not including the upper limit.
Following the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- The length of a pencil is 15·4 cm to the nearest millimetre.
Write down the lowest possible length of the pencil.
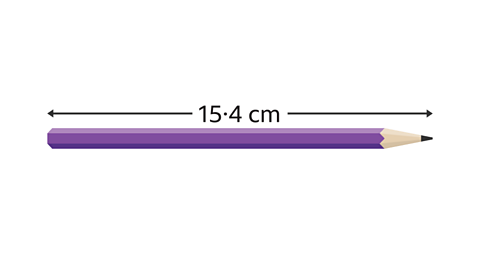
The lowest possible length of the pencil is 15·35 cm.
The pencil length is given to 1 decimal place, the nearest 0·1.
0·1 ÷ 2 = 0·05
The lowest possible length is 15·4 – 0·05 = 15·35 cm.
- A swimmer wins the 400 m front crawl with a time of 43·85 seconds.
Write the error interval for this time.

43⋅845 ≤ 43∙85 < 43∙855

The time is given to the nearest 0·01.
- 0·01 ÷ 2 = 0·005
To calculate the lower limit: 43∙85 − 0∙005 = 43∙845
To calculate the upper limit: 43∙85 + 0∙005 = 43∙855
Check your understanding
Quiz - Accuracy in maths
Practise what you've learnt about accuracy in maths in this quiz. The questions change each time you try, so keep testing your knowledge.
Video – Upper and lower bounds
Watch this video to find out how to calculate upper and lower bounds.
Upper and lower bounds.
Higher tier.
In any measurement, there's always some level of uncertainty or error.
For example, a basic ruler shows this pencil to be 11 centimetres long, to the nearest centimetre. But a ruler with more precise measurements will give a less rounded value, of 10.8 centimetres, to the nearest millimetre.
For any given measurement, there's a lower and upper bound to what the actual, non-rounded measurement could be.
To work out these bounds, think about the place value you're rounding to.
In this case, the pencil is measured as 11 centimetres, to the nearest centimetre.
So, use a number line that includes the rounded value 11, and one unit either side. So, 1 centimetre less and 1 centimetre more than 11, which would be 10 and 12.
Now, consider the midpoints between these, and the measured value, 10.5 and 11.5. These midpoints are the lower and upper bounds. Which means anything between them rounds to 11, but anything either side of them, on this number line, rounds to either 10 or 12, to the nearest centimetre.
This can be shown using inequality symbols.
Where a less than or equal to symbol shows that the lower bound is included in values that round to 11, to the nearest centimetre. And a strict less than symbol, shows that the upper bound is not included, since 11.5 would round up to 12.
Let's look at an example question:
The sides of a square are measured as 5.3 centimetres, to the nearest 0.1 centimetres. Work out the lower and upper bounds for the area of the square.
The precision is 0.1 centimetres, so consider a number line that includes the values either side of 5.3 to the nearest 0.1 centimetres, that's 5.2 and 5.4.
The midpoint between these values and the measured value are 5.25 and 5.35.
the lower bound for the length is 5.25 centimetres, and the upper bound is 5.35 centimetres.
But be careful!
This isn't the final answer, as the question asks you to find the lower and upper bounds for the area of the square.
To find the area of a square, you square the side lengths. Which means you need to square each of the lower and upper bounds.
So, the lower bound for the area is 5.25 squared, which equals 27.5625 centimetres squared. And the upper bound is 5.35 squared, which equals 28.6225 centimetres squared.
Let's write this using inequalities:
The area is greater than or equal to 27.5625 centimetres squared, but less than 28.6225 centimetres squared.
Higher - What are upper and lower bounds?
The lower bound is the smallest, lowest or minimum value.
The upper bound is the largest, greatest or maximum value.
To find the upper and lower bounds of a rounded number, 𝑛:
Identify the degree of accuracy (place value) to which the number has been rounded.
Halve the degree of accuracy:
Add to the number for the upper bound (maximum).
Subtract from the number for the lower bound (minimum).
The symbol ± may be used to show that the same amount is added and subtracted.
To find the upper and lower bounds for a truncated number, 𝑛:
Upper bound:
Increase the final digit by 1, for a number with decimal digits.
Increase the last non-zero digit by 1, for a whole number.
Lower bound:
- Use the number itself.
The error interval is written as lower bound ≤ 𝑛 < upper bound.
𝑛 can take any value from the lower bound, up to but not including the upper bound.
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Write the error interval for 𝑥.
𝑥 = 12·83
12·825 ≤ 𝑥 < 12·835
𝑥 has been written to the nearest 0·01.
0·01 ÷ 2 = 0·005
The upper bound is 12·83 + 0·005 = 12·835.
The lower bound is 12·83 – 0·005 = 12·825.
- A number 𝑛 is to one digit, 6.
Write the error interval for 𝑛.
6 ≤ 𝑛 < 7
When a number is truncated, the subsequent digits are not used.
The lower bound is the number itself (6).
The upper bound is 6 + 1 = 7.
Higher - How to apply and interpret upper and lower bounds
The lower bound is the smallest, lowest or minimum value.
The upper bound is the largest, greatest or maximum value.
To work out the upper or lower bounds of a calculation involving two numbers, learn when to use the same bounds and when to use different bounds.
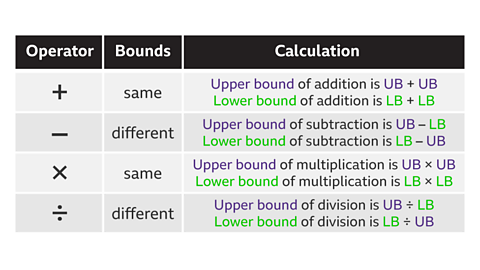
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- The numbers 𝑥 and 𝑦 are given to the nearest integer. Find the least possible value of \(\frac{x}{y}\).
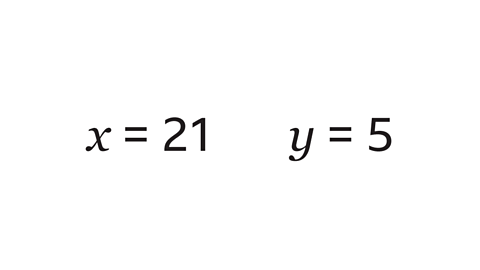
The least value of \(\frac{x}{y}\) is 3·7272727272… (which can be written as \(3· \dot{7} \dot{2}\).
The least value is found by dividing the lower bound of 𝑥 by the upper bound of 𝑦.
The values are given to the nearest integer (1).
Lower bound of 𝑥 is 21 – 0·5 = 20·5.
Upper bound of 𝑦 is 5 + 0·5 = 5·5.
The least value of \(\frac{x}{y}\) is 20·5 ÷ 5·5 = 3·7272727272… (or \(3· \dot{7} \dot{2}\)).
- The width of a rectangular field is 44 m, measured to the nearest metre.
The length of the field is 105 metres, measured to the nearest 5 metres.
Work out the upper bound for the perimeter of the field.
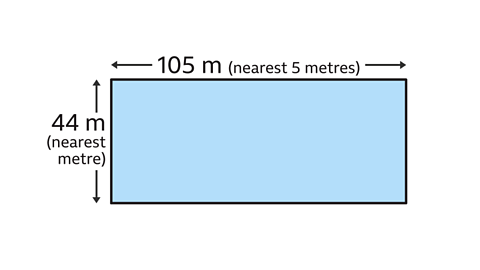
The upper bound for the perimeter is 304 m.
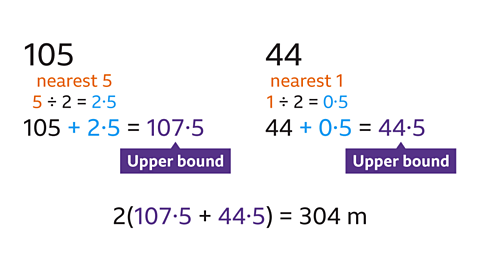
The upper bound of the perimeter is the sum of the upper bounds of each side of the field.
The upper bound for the width is 44 + 0·5 = 44·5 m.
The upper bound for the length is 105 + 2·5 = 107·5 m.
The perimeter is 2(length + width):
- 2(107·5 + 44·5) = 304 m.
Higher - Quiz - Upper and lower bounds
Practise what you've learned about upper and lower bounds in this quiz for Higher. The questions change each time you try, so keep testing your knowledge.
Now you've revised what accuracy is in maths, why not check out standard form?
More on Number
Find out more by working through a topic
- count8 of 15

- count10 of 15
