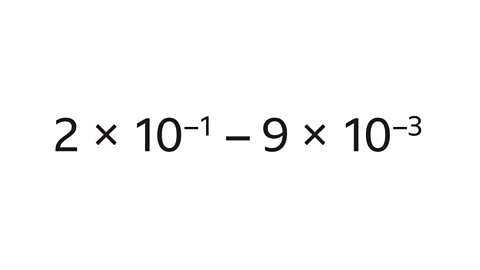Key points
standard formStandard form is a way to write really large or very small numbers. In standard form, numbers are recorded as a number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of ten. This is also called standard index form or scientific notation. is a way of writing very large and very small numbers so that they are easier to understand and work with. It is also called standard index form or scientific notation.
Any number in standard form is written as:
A × 10ⁿ
A is a number that is equal to or greater than 1 and less than 10, n is the integerIntegers are numbers with no fraction or decimal part. They can be positive, negative or zero. 42, 8, and 10000 are examples of integers. powers of 10The second power of 10 for example is 100. Powers of 10 are 10, 100, 1000 and so on. to multiply by to get the original value.
For example, 300 in standard form would be 3 x 10². A = 3 and n = 2
The integer power of ten is positive for numbers greater than 10 and negative for values less than 1. For numbers that are between 1 and 10, the integer power of ten is zero.
It is useful to have a good understanding of place value as well as multiplying and dividing by powers of ten.
Video
Standard index form is used in computer game design.
Watch the video to listen to games developer Shahan describe how he uses standard index form in his work.
Bobby: Hi, Shahan.
Shahan: Hi, Bobby.
Bobby: You're a games developer, right?
Shahan: I am indeed, so I’m a programmer which means I use computer language and maths to develop games.
Bobby: So, tell me about a game you’ve been working on recently.
Shahan: So, recently I’ve been making a game called Stellar, where you travel across space to fight aliens using nanotechnology.
Bobby: Nanotechnology, that’s really small, right?
Shahan: Really, really small and in fact, if I was to write it down by hand, it would take me absolutely ages. The same with typing out, so what we do for our nanotechnology is define it as eight times ten to the power of minus nine.
Bobby: That’s standard index form! So, mathematically, it would be the decimal point followed by eight zeros, then the number.
Shahan: Exactly, and we also use it to write out really huge numbers as well. For example, in our game, we’ve set our alien planet as three times ten to the power of fifteen kilometres away from Earth. So that’s another standard index form to make it a lot simpler for us.
Bobby: So, where else might you see maths turn up in your work?
Shahan: Absolutely everywhere. I mean, there’s all sorts of maths all across game development. Algebra, for example, is fundamental when it comes to coding. Lots of languages use algebra to substitute in big numbers, small numbers for letters and that just makes our lives a lot easier.
Bobby: So I can see now how standard index form and, indeed, maths can make your life simpler as a games developer.
Shahan: Exactly.
How to write numbers in standard form
To write a number in standard formStandard form is a way to write really large or very small numbers. In standard form, numbers are recorded as a number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of ten. This is also called standard index form or scientific notation. :
Write the number as a value between 1 and 10. The first non-zero digit is in the units column, followed by the decimal point and the remaining digits. Zeros at the end of the number are not needed. For a single digit value, the decimal point is not needed.
Write × 10
Write in the powers of 10The second power of 10 for example is 100. Powers of 10 are 10, 100, 1000 and so on. .
For a number greater or equal to 10, the power is a positive integerIntegers are numbers with no fraction or decimal part. They can be positive, negative or zero. 42, 8, and 10000 are examples of integers..
- The power can be found by counting the number of places the first non-zero digit has moved to the right.
- This is the number of times the value must be multiplied by 10 to get the original number.
- For example, 1000 is greater than 10, so the power is positive. 1000 in standard form is 1 x 10³
For a number greater or equal to 1 and less than 10, the power is zero.
- For example, 4 is greater than 1 but less than 10, so the power is zero. 4 in standard form is 4 x 10⁰
For a number less than 1, the power is a negative integer.
- The power can be found by counting the number of places the first non-zero digit has moved to the left.
- This is the number of times the value must be multiplied by \( \frac{1}{10} \) (or divided by 10) to get the original number.
- For example, 0∙001 is less than 1, so the power is negative. 0.001 in standard form is 1 x 10⁻³
Examples

Image caption, Write 800,000 in standard form.

Image caption, Write the number (800,000) as a value between 1 and 10. The first non-zero digit (8) is in the units column, followed by the decimal point and the rest of the digits. Zeros after the 8 are not needed. For a single digit value, the decimal point is not needed.
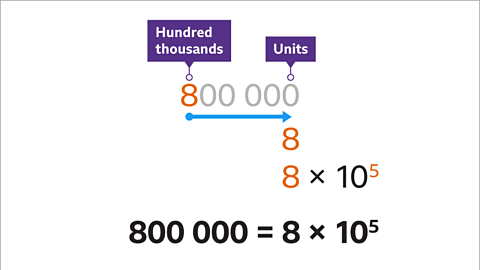
Image caption, Write × 10. Write in the power of ten. The power is a positive integer because 800,000 is greater than 10. The power can be found by counting the number of places the first non-zero digit has moved to the right. The digit 8 has moved from the hundred thousands place value column to the units column. This is five places. 800,000 is 8 × 10⁵ in standard form.

Image caption, Write 3∙9 in standard form.

Image caption, Write the number (3∙9) as a value between 1 and 10. The first non-zero digit (3) is in the units column, followed by the decimal point (3∙9). The number is already between 1 and 10
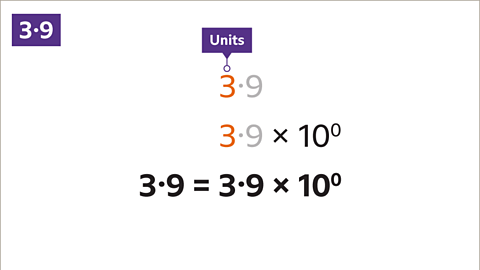
Image caption, Write × 10. Write in the power of ten. The power can be found by counting the number of places the first non-zero digit has moved to the right. The digit 3 has not moved, and is already in the units place value column. The power of ten is zero. 3∙9 is 3∙9 × 10⁰ in standard form.

Image caption, Write 0∙007601 in standard form.

Image caption, Write the number (0∙007601) as a value between 1 and 10. The first non-zero digit (7) is in the units column, followed by the decimal point.

Image caption, Write × 10. Write in the power of ten. The power is a negative integer because 0∙007601 is less than 1. The power can be found by counting the number of places the first non-zero digit has moved to the left. The digit 7 has moved from the thousandths place value column to the units column. This is three places. 0∙007601 is 7∙601× 10⁻³ in standard form.
1 of 9
Question
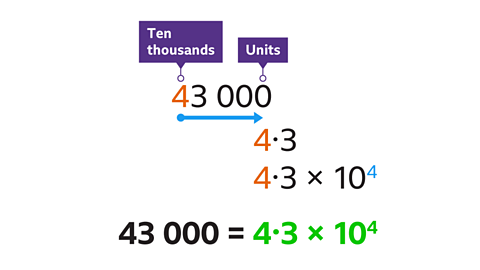
Write 43,000 in standard form.
Write the number (43,000) as a value between 1 and 10. The first non-zero digit (4) is in the units column, followed by the decimal point and the remaining digits (3). Zeros at the end of the number are not needed. The number is 4∙3
Write × 10. Write in the power of ten. The power is a positive integer. The power can be found by counting the number of places the first non-zero digit has moved to the right (4 places). This is the number of times the value (4∙3) must be multiplied by 10 to get the original number.
43,000 is 4∙3 × 10⁴ in standard form.
How to convert from standard form to an ordinary number
To convert a standard form number (A × 10ⁿ) to an ordinary (decimal) number, multiply the value A by the power of ten:
Where n is positive, the number is larger than A.
- Each digit in A moves n places to the left.
- Gaps between the digits of A and the decimal point are filled with place holder zeros.
Where n is negative, the number is smaller than A.
- Each digit in A moves n places to the right.
- Gaps between the digits of A and the decimal point are filled with place holder zeros.
Where n is zero the ordinary number is the value of A.
Examples
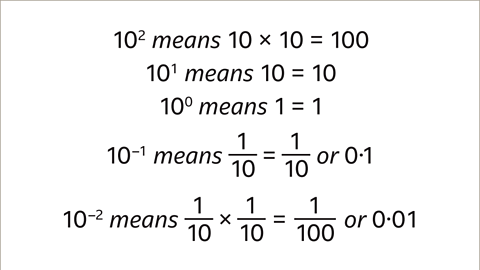
Image caption, Powers of ten.
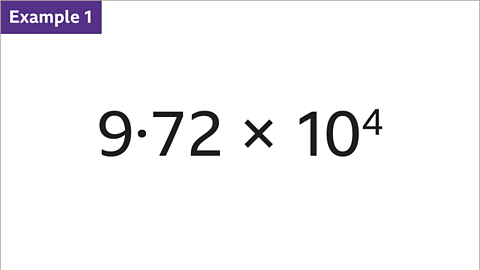
Image caption, Write 9∙72 × 10⁴ as an ordinary (decimal) number.

Image caption, Multiply A (9∙72) by the power of ten (10⁴). 10⁴ means 10 × 10 × 10 × 10 or 10,000
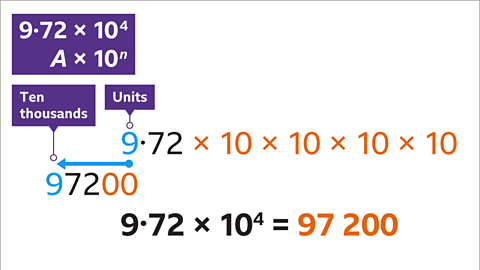
Image caption, To multiply by 10,000 move each digit four places to the left. 9 units become 9 ten-thousands (90,000). 7 tenths become 7 thousands and 2 hundredths become 2 hundreds. Fill in gaps before the decimal point with two place holder zeros so that the number has the correct value. Write the answer clearly.
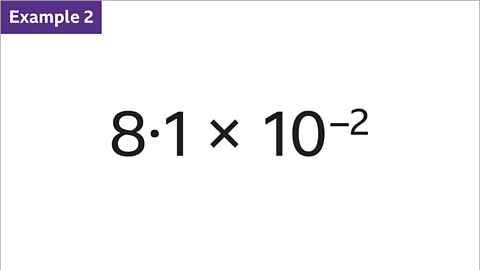
Image caption, Write 8∙1 × 10⁻² as an ordinary (decimal) number.
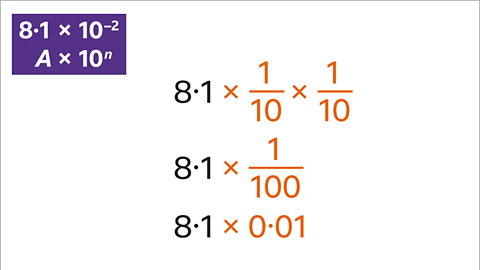
Image caption, Multiply A (8∙1) by the power of ten (10⁻²). 10⁻² means 1⁄10 × 1⁄10 or 1⁄100 or 0∙01
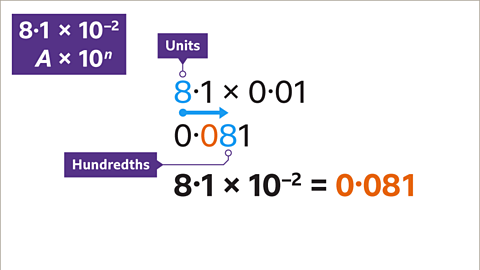
Image caption, To multiply by 0∙01 move each digit two places to the right. 8 units become 8 hundredths (0∙08) and 1 tenth become 1 thousandth. Fill in the gap before the decimal point with a place holder zero so that the number has the correct value. Write the answer clearly.
1 of 7
Question
30 pies are sold for £45. How much do 5 pies cost?
The number of pies and the cost of the pies are directly proportional.
To find out how much 5 pies cost, work out how many times 5 goes into 30:
30 ÷ 5 = 6
The number of pies has been divided by 6. The cost now also needs to be divided by 6:
The cost of 5 pies is 45 ÷ 6
45 ÷ 6 = 7∙5
The cost of 5 pies is £7.50

How to compare and order numbers in standard form
To compare and order numbers in standard form:
- Start with the power of ten.
- The greater the power of ten, the greater the order of magnitudeThe approximate size, often given as a power of 10. Magnitude means size. of the number.
- If some numbers have the same power of ten, use the value of A to compare them. Use understanding of ordering decimals for this process.
It may be useful to review comparing and ordering decimals
Examples
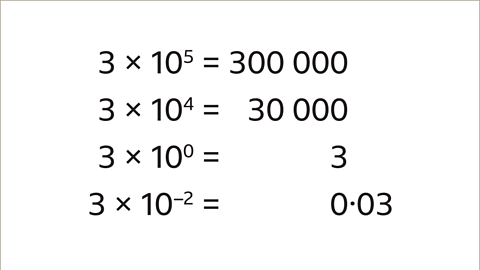
Image caption, The greater the power of ten, the greater the number.

Image caption, Order these values from smallest to greatest.

Image caption, Look at the powers of ten. The larger the power of ten, the greater the magnitude of the number. 3∙4 × 10⁷ is the greatest number because it has the greatest power of ten. 8 × 10⁻² is the smallest number because the power of ten is the least.
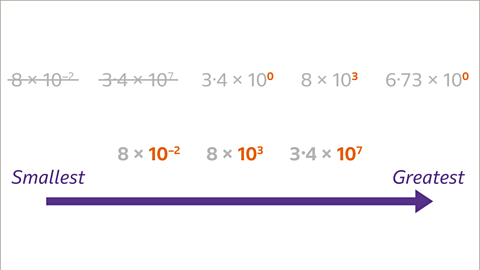
Image caption, 8 × 10³ is the next biggest number because 10³ is greater than 10⁰
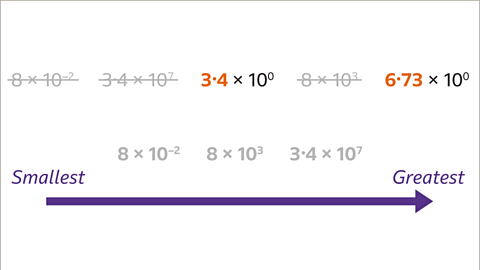
Image caption, 3∙4 × 10⁰ and 6∙73 × 10⁰ have the same order of magnitude, so the numbers are compared using the value of A. 3∙4 is less than 6∙73, so 3∙4 × 10⁰ is less than 6∙73 × 10⁰

Image caption, The numbers are now in ascending order from smallest to greatest.
1 of 6
Standard form
Quiz
Try this activity to practise ordering numbers in standard form.
Quiz
Try this quiz to practise what you have learned about standard form. You might need a pen and paper to help with your working out.
Real-world maths
Standard form is used by astrophysicists to manage extremely large numbers, including the speed of light (3 x 10⁸ m/s) and the distance between planets, moons and asteroids. Chemists use standard form notation both for large values such as Avogadro’s constant (6 x 10²³) which is the number of atomThe smallest particle of an element. Atoms are made from small particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. in a a moleA standard scientific unit for measuring a number of atoms, ions or molecules. It is a large number: 6 x 10²³ , as well as for very small measurements like the distance between sub-atomic particles.

For extreme distances, specialist units for example, light years may be used, which is how far light travels in one year (approximately 9.46 × 10¹⁵ km), and a femtometre which is 1 x 10⁻¹⁵ metres, which is used to measure extremely small things, such as the nucleusThe central positively charged part of the atom/ion. The nucleus contains the protons and neutrons. of an atom.
For extreme distances, specialist units may be used like light-years, which is how far light travels in one year (approximately 9 × 10¹⁵ km), and a femtometre which is 1 x 10⁻¹⁵ metres and is the approximate length of a quark (a subatomic particle).

Game - Divided Islands
Play the Divided Islands game! gamePlay the Divided Islands game!
Using your maths skills, help to build bridges and bring light back to the islands in this free game from BBC Bitesize.

More on Standard index form
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 2