Key points about how to round numbers

Numbers can be by (to) roundIn the context of a number, express to a required degree of accuracy, eg 543 rounded to the nearest 10 is 540. when it is not necessary to give an exact value. This makes a number simpler but keeps it close to its original value.
Numbers may be rounded in different ways, including to the nearest whole number, a given number of or , or by .
Use rounded values to the answer to a calculation. This is a useful non-calculator skill.
Refresh your knowledge with these guides on rounding and significant figures.
Video – Rounding to significant figures
Watch this video to find out how and why we round numbers to significant figures.
Rounding to significant figures.
It's sometimes useful to give a value to a certain number, of significant figures.
For example, 21.13467025 degrees might be rounded to 20 degrees, to 1 significant figure, or 21 degrees, to 2 significant figures in a weather report.
The more significant figures you give, the closer you get to the actual value.
When rounding to a given number of significant figures, it's important to know what place value you're rounding to, for example, to the nearest ten, hundredth, or ten thousandth.
Let's look at some examples.
Question 1 says: Round 0.004073 to 2 significant figures.
The first significant digit is 4, in the thousandths place value, because there are no ones, tenths, or hundredths.
Since you're rounding to 2 significant figures, you need to round to the nearest ten-thousandth.
It's important to remember that any number after the first significant figure, is considered a significant figure, even if the number is zero.
Looking at this on a number line, the original value is somewhere between 0.0040 and 0.0041, to the nearest ten thousandth.
In between these, is the middle value of 0.00405.
0.004073 is greater than this middle value, meaning it rounds up to 0.0041, to 2 significant figures.
In general, if the next digit along from the place value you're rounding to, in this case, the third significant figure, is a 5 or more, the number rounds up, but if it's a 4 or less, the number rounds down.
So, to 2 significant figures, 0.00405 would round up to 0.0041.
For the next question, round 2394 to 3 significant figures.
This time, the first significant figure is 2, the second is 3, and the third is 9.
Again, thinking about the place value columns, 9 is in the tens column so it will round to the nearest 10, either 2390 or 2400.
On a number line, 2394 is less than 2395. So, it must round down to 2390, to 3 significant figures.
Check your understanding
What is approximation?
Approximation is rounding a number to a simpler value.
To round to a given place value (eg the nearest hundred or nearest tenth):
Identify the given place value digit (such as hundreds or tenths).
Look at the next digit to the right:
Round down if it is less than 5. The given place value digit remains the same.
Round up if it is 5 or more. The given place value digit increases by 1.
Consider the given place valueThe value of a digit that relates to its position or place in a number, eg in 1482 the digits represent 1 thousand, 4 hundreds, 8 tens and 2 ones. of the rounded digit (eg nearest hundredth):
When the given place value is 10 or more, write zeros after the rounded digit in order to retain the of the number.
When the given place value is a decimal, the rounded digit is the final digit of the written number.
If the digit in the given place value column is nine and is rounded up, a zero is written and 1 is added to the digit to the left.
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Which two of these numbers will round to 820 when rounded to the nearest 10?
825 823∙4 816 814·9
823·4 and 816 both round to 820 to the nearest 10.
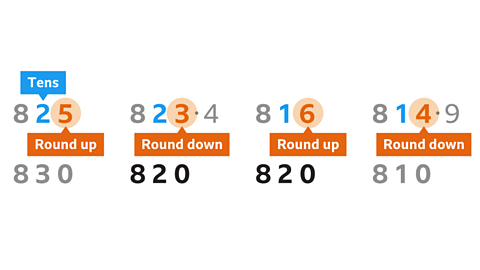
In 823·4, the 3 does not round up the 2, so 823·4 rounds down to 820 to the nearest 10.
In 816, the 6 rounds the 1 up to 2, so 816 rounds up to 820 to the nearest 10.
In 825, the 5 rounds the 2 up to 3, so 825 rounds up to 830 to the nearest ten.
In 814·9, the 4 does not round up the 1, so 814·9 rounds down to 810 to the nearest ten.
This can also be checked on a number line.
- Round 4∙5817 to the nearest thousandth.
4∙5817 = 4∙582 to the nearest 1000th.

The digit 1 is in the thousandths column.
The next digit to the right is 7.
7 is greater than 5 and will round up the 1 to 2.
How to round a number to decimal places
To round a number to a given number of decimal places:
Count digits after the decimal point to the digit you are rounding to.
Leave it the same if the next digit is less than 5 (this is called rounding down).
Increase it by 1 if the next digit is 5 or more (this is called rounding up).
Use a number line when rounding numbers as a helpful way of visualising whether a number is closer to one value or another.
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Round 58·1666 to 2 d.p.
58·1666 = 58·17 to 2 d.p.
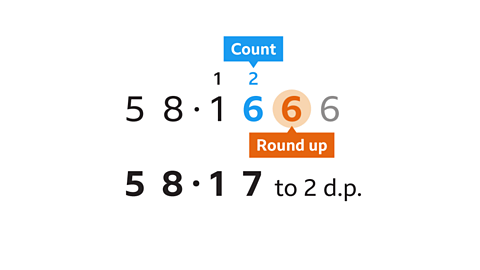
Count to the second place of decimals, which is 6.
The next digit is also a 6, greater than 5, so 1 is added to the second decimal place.
The number has been rounded up.
- Round to 0·02222 to 3 decimal places.
0·02222 = 0·22 to 3 d.p.
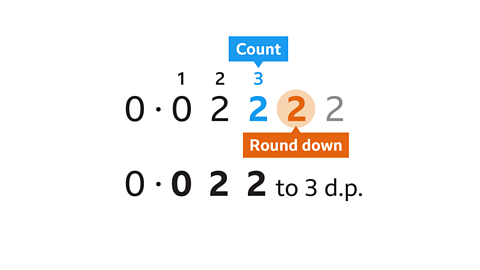
Count to the third place of decimals, this is 2.
The next digit is also a 2, which is less than 5 so the third decimal place does not change.
The number has been rounded down.
How to round a number to significant figures
To round to a given number of significant figures:
Identify the first significant figure, which is the first non-zero digit.
Count to find the significant figure for the degree of accuracy required. The next digit to the right will determine the rounding:
Less than 5 – the significant digit does not change.
5 or more – round up by adding 1 to the significant digit.
Check that the number remains the same .
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Round 234 to 1 significant figure.
234 = 200 to 1 s.f.

The first significant figure is the first non-zero digit (2).
The next digit to the right (3) determines the rounding.
3 is less than 5 so the 2 does not change.
- Round 0·05072 to 2 significant figures.
0·05072 = 0·051 to 2 s.f.
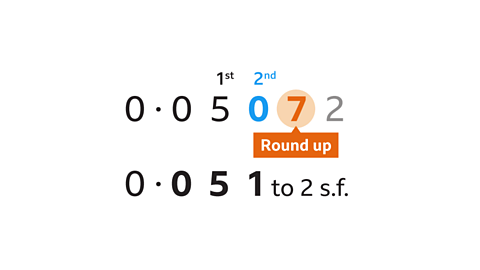
The first significant figure is the first non-zero digit (5).
Count to find the 2nd significant figure, this is 0.
The next digit to the right (7) determines the rounding.
7 is greater than 5 so 1 is added next to the 5.
Significant figures - interactive activity
This interactive activity will help you see how numbers are rounded to different significant figures.
What is truncation?
To a number at a particular place value:
Identify the required place value digit.
Remove digits to the right of the required place value digit.
Replace digits between the truncated place value digit and the decimal point with zeros.
Truncation always rounds a number down, no matter the size of the digit to the right of the place value digit.
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Truncate 0·096501 to 2 significant figures.
0·096501 = 0·096 truncated to 2 s.f.
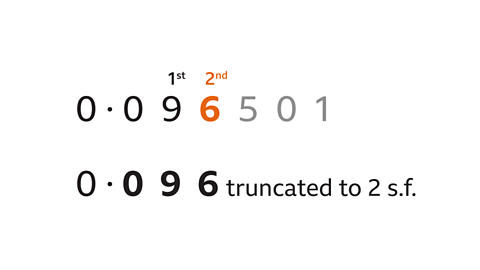
The first significant figure is the first non-zero digit (9).
Count to the second significant figure.
The rest of the digits are not used.
- Truncate 6·084 to 1 decimal place.
6·084 = 6·0 truncated to 1 d.p.

Count to the first place of decimals (0).
The rest of the digits are not needed and are not written.
A truncated number is always rounded down.
How to estimate calculations
To estimate calculations using rounded values:
Round each number in the calculation to one significant figure.
Use the rounded values to work out the answer.
It is sometimes possible to state whether the estimate is an overestimate or an underestimate. Sometimes it is difficult to tell which.
The symbol ≈ is used to say that one value is approximately equal to another.
Follow the working out below
GCSE exam-style questions
- Bryn is paid £13.40 for each hour he works.
Bryn works for 31 hours in a week.
Work out an estimate for his pay in one week.
Bryn earns approximately £300: 10 × 30 = 300.
Each number is rounded to 1 significant figure.
13·40 rounds to 10 and 31 rounds to 30.
13·41 × 31 is approximately 10 × 30 = 300.
Both numbers have been rounded down so £300 is an underestimate.
- Work out an estimate for the value of:
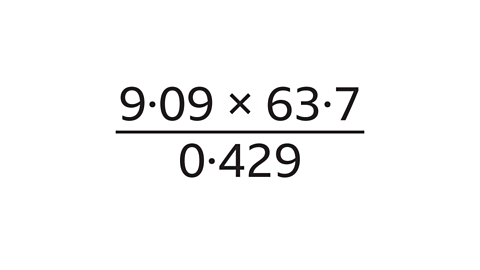
The answer is approximately 1350.
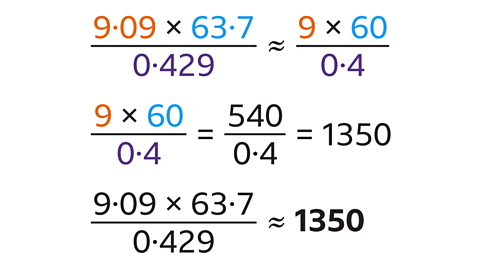
9·09 = 9 to 1 s.f.
63·7 = 60 to 1 s.f.
0·429 = 0·4 to 1 s.f.
9 × 60 ÷ 0·4 = 1350
Quiz - Rounding numbers
Practise what you've learned about rounding numbers with this quiz. The quiz questions change each time you try, so keep testing your knowledge.
Now you've revised how to round whole numbers, why not try learning about laws of indices?
More on Number
Find out more by working through a topic
- count7 of 15

- count8 of 15

- count10 of 15
