What are the key learning points about heat transfer?
Heat can be transferred from place to place by conductionThe transfer of heat through a material by transferring kinetic energy from one particle to another. convectionThe transfer of heat energy through a moving liquid or gas. and heat radiationThis is when heat energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves generated by an object's temperature. Unlike conduction and convection, this type of heat transfer occurs even in the absence of a medium, such as in a vacuum..
The transfer of energy by conduction and convection involves particlesAll substances are made of particles. Particles could be atoms, molecules or ions..
Metals are the best conductors of heat because they contain free electronsNegatively charged sub-atomic particles that can move through the structure of a substance, usually a metal or graphite. A material with many free electrons is a good conductor..
Convection occurs in liquids and gases.
The transfer of energy by radiation does not require particles.
Dark matt surfaces are better at absorbing and radiating heat energy than light shiny surfaces.
Heat energy can be lost from homes mainly through conduction and convection, but these losses can be reduced by methods of insulationA layer put around a building or in a roof space to retain heat during colder weather or to keep a building cool during warmer weather..
What is the difference between temperature and heat?
Temperature and heat are not the same thing because:
Temperature is a measure of how hot something is.
Heat is a measure of the thermal energy contained in an object.
Temperature is measured in oC.
Heat energy is measured in J.
Key fact
Heat energy can flow by conductionThe transfer of heat through a material by transferring kinetic energy from one particle to another., convectionThe transfer of heat energy through a moving liquid or gas. or heat radiationThis is when heat energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves generated by an object's temperature. Unlike conduction and convection, this type of heat transfer occurs even in the absence of a medium, such as in a vacuum..
It always flows from a region of high temperature to a region of low temperature i.e. from hot to cold.
What are good conductors of heat energy?
Metals are good conductor (energy)A material which allows heat energy to move easily by conduction. Metals are good conductors because they contain free electrons. of heat energy.
Non-metals and gases are usually poor conductors.
Poor conductors are called insulators.
Heat energy is conducted from the hot end of an object to the cold end.
Conduction in solids
The atomAll elements are made of atoms. An atom consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. of a solid are held together by chemical bonds.
The atoms are fixed in place but are free to vibrate.
When part of a solid absorbs heat energy the atoms vibrate faster and with bigger amplitude.
These vibrations pass from atom to atom transferring heat energy as they do so.
This process happens in all solids when heated but is a slow process.
Conduction in metals
Some of the electronSubatomic particle, with a negative charge and a very small mass relative to protons and neutrons. in a piece of metal can leave their atoms and move about in the metal as free electronsNegatively charged sub-atomic particles that can move through the structure of a substance, usually a metal or graphite. A material with many free electrons is a good conductor..
The parts of the metal atoms left behind are now positively charged metal ionElectrically charged particle, formed when an atom gains or loses electrons..
When the free electrons absorb heat energy, they move much faster.
As they move through the metal, free electrons crash into metal ions.
Some of the kinetic energyEnergy which an object possesses by being in motion. of the free electron is absorbed by the ions and it vibrates faster and with greater amplitude.
This process is very much faster than conduction caused by just passing vibrations from atom to atom.
Hence, conduction in metals is faster than in non-metals.
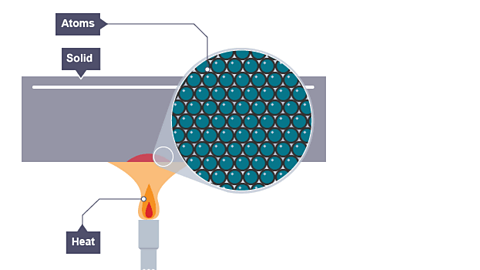
Image caption, Conduction in a solid
A solid is heated up
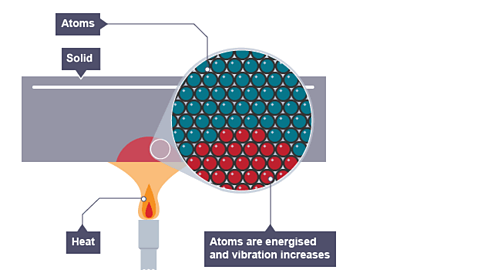
Image caption, Conduction in a solid
The heat energises the atoms and vibration increases
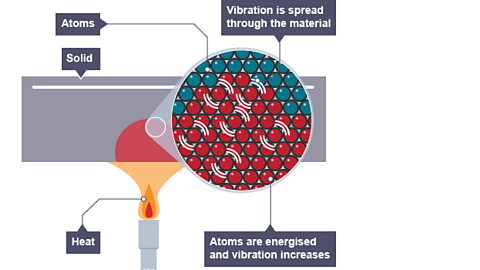
Image caption, Conduction in a solid
The vibration spreads throughout the solid heating up the entire bar but this is a very slow process
1 of 3
Key points
Conduction in insulators (non-metals) is only caused by passing vibrations from atom to atom.
Conduction in good conductors (metals) is caused by collisions between fast moving free electrons and metal ions and by passing vibrations from atom to atom.
Conduction by collisions between fast moving free electrons is very much faster than conduction by passing vibrations from atom to atom.
Metals are good conductors because they contain free electrons.
How to investigate conductors experimentally
An experiment can be used to investigate which metal is the best conductor (energy)A material which allows heat energy to move easily by conduction. Metals are good conductors because they contain free electrons. of heat.
It involves some long thin strips of different metals (eg iron, aluminium and copper), Vaseline, drawing pins and a Bunsen burner.
Method
Fix the drawing pin to the end of the metal strip using spots of Vaseline.
Position the other end of the metal strip into a Bunsen flame.
Record the time taken for the Vaseline to melt and the drawing pin to drop off.
The fastest time shows the best conductor of heat.
In this experiment:
Independent variable: the material of the metal rod.
Dependent variable: the time taken for the Vaseline to melt and the drawing pin to drop off
Control variables: length of metal rod, diameter of rods, position in the Bunsen flame, mass of drawing pin and quantity of Vaseline.
The drawing pin falls off the copper rod first followed by the aluminium.
From this we can conclude that copper conducts better than aluminium, while aluminium conducts better than iron and brass.
How does convection occur in liquids and gases?
Heat can be transferred in liquids or gases by convectionThe transfer of heat energy through a moving liquid or gas..
Fluids
Liquids and gases are fluids because they can be made to flow.
The particleA general term for a small piece of matter. For example, protons, neutrons, electrons, atoms, ions or molecules. in these fluids can move from place to place.
Convection occurs when particles with a lot of heat energy in a liquid or gas move and take the place of particles with less heat energy.
Convection in a liquid
Convection in a liquid can be seen by putting a crystal of potassium permanganate in a beaker of water and gently heating it with a Bunsen flame.
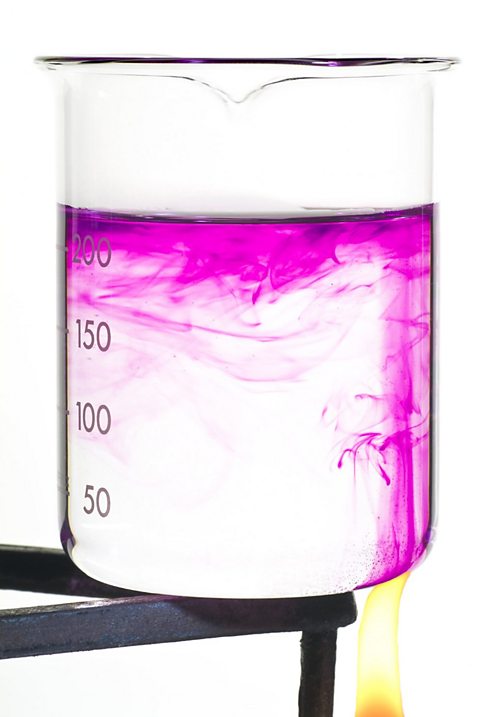

Results
Heat is initially transferred through the glass wall of the beaker by conductionThe transfer of heat through a material by transferring kinetic energy from one particle to another..
The water in the region of the Bunsen flame is heated.
It expands, becomes less dense and rises.
It is replaced by the cooler, denser water which surrounds it.
This water is in turn heated, expands becomes less dense and rises.
The process continues, a convection current is set up and heat is transferred through the liquid.
convectionThe transfer of heat energy through a moving liquid or gas. currents can be seen in lava lamps.
The wax inside the lamp warms up, becomes less dense than the liquid and so rises.
Convection in a gas
How do radiators generate convection currents?
Air close to the radiator is heated.
It expands, becomes less dense and rises.
It is replaced by the cooler, denser air which surrounds it.
This air is in turn heated, expands becomes less dense and rises.
The process continues, a convection current is set up and heat is transferred through the air and hence through the room.
Convection currents enable hot air balloons to rise, and also explain why it is often hotter in houses upstairs rather than downstairs.
Most of our winds are caused by convection currents occurring on a big scale in air.
Many ocean currents are also due to convection currents.
How is heat energy transferred by radiation?
Heat can be transferred by infrared radiation.
Unlike conduction and convection - which need the vibration or movement of particleA general term for a small piece of matter. For example, protons, neutrons, electrons, atoms, ions or molecules. - infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation.
When infrared radiationElectromagnetic radiation emitted from a hot object. is absorbed (taken in) by an object it is heated and its temperature rises.
When infrared radiation is emitted by an object it loses heat energy and its temperature decreases.

Because no particles are involved, heat radiationThis is when heat energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves generated by an object's temperature. Unlike conduction and convection, this type of heat transfer occurs even in the absence of a medium, such as in a vacuum. can work through the vacuumA volume of space that contains no matter. of space.
This is why we can still feel the heat of the Sun even though it is 150 million km away from the Earth.
How to investigate the emission of heat radiation experimentally
The transfer of infrared radiation from a hot object to cooler surroundings can be investigated using a piece of apparatus called Leslie’s cube.
This is a metal cube with four sides prepared in different ways: black, white, shiny, or dull.
It can be filled with hot water or heated on an electrical hot plate so that all four sides are at the same temperature.
Method
Measure the temperature a fixed distance from each side of a Leslie's cube using four identical thermometers.
Heat the Leslie’s cube by filling it with boiling water.
Continue to measure and record the temperatures every 30 seconds for five minutes, then plot a graph of temperature on the y-axis, against time on the x-axis, for each side.
Compare the four graphs obtained.
In this experiment:
Independent variable: the type of surface of the side
Dependent variable: the temperature rise of each surface
Control variables
Distance of each thermometer from the sides of the cube, the type of thermometer used and the time taken for each reading.
Results
The temperature of the thermometer opposite the dull, black side reaches the highest temperature in the same time interval.
From this we can say that dark matt surfaces are better at radiating heat energy than light shiny surfaces.
Key point
- Dark matt surfaces are better at radiating heat energy than light shiny surfaces.
| Surface | Absorption | Emission |
|---|---|---|
| Dull, matt or rough | Good absorber of heat radiation | Good emitter of heat radiation |
| Shiny | Poor absorber of heat radiation | Poor emitter of heat radiation |
Radiators are often painted with gloss paint, but they would be better at radiating heat if they were painted with matt black paint instead.
They are painted white to make them look nicer.
However, despite their name, radiators actually transfer most of their heat to a room by convection, not radiation.
Normally radiant heaters must be at least red hot before they are effective.
Experiment: Absorption of heat radiation
When an object absorbs radiation, it heats up and its temperature will rise.
You feel the heat of the sun when you absorb the infrared radiation from it.
If a cloud passes in front of the sun, you absorb less infrared, and it feels cooler.
How infrared radiation is absorbed can be investigated using the apparatus shown below.
Two squares of aluminium are arranged as shown above.
One is painted dull black, the other is polished and shiny.
To ensure a fair test they are the same area and thickness and are placed the same distance from the Bunsen flame.
Two identical corks are stuck to the back of the plates using equal amounts of Vaseline or candle wax (control variables).
The Bunsen is lit.
Quite quickly the cork attached to the black plate falls off.
The cork behind the polished plate takes much longer to fall off.
Conclusion
Both plates receive the same quantity of radiation, but the black plate heated up more quickly.
This tells us that a dull, black surface is a better absorber of radiation than a shiny, polished surface.
Key points
- Dark matt surfaces are better at absorbing heat energy than light shiny surfaces.
How can heat transfers be reduced in houses?
Heat energy is lost from buildings through their roofs, windows, walls, floors and through gaps around windows and doors.
However, there are ways that these losses can be reduced.
What are the main heat escape routes in a house?
Take a look at this thermogram of a house.
The roof and windows are the hottest, showing that most heat is lost from the house through those parts.

Heat energy is transferred from homes by conductionThe transfer of heat through a material by transferring kinetic energy from one particle to another. through the walls, floor, roof and windows.
It is also transferred from homes by convectionThe transfer of heat energy through a moving liquid or gas..
For example, as hot air in rooms rise, cold air can enter the house through gaps in doors and windows to replace it.
These convection currents can transfer heat energy into the loft.
Heat energy also leaves the house by heat radiationThis is when heat energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves generated by an object's temperature. Unlike conduction and convection, this type of heat transfer occurs even in the absence of a medium, such as in a vacuum. - through the walls, roof and windows.
Where does heat loss occur in a house?
What are ways of reducing heat loss in a house?
Key fact
- Trapped air is a natural insulator and because it is trapped, convection currents cannot be set up easily. So, trapped air reduces heat loss by conduction and convection. Many insulating materials incorporate trapped air.
There are several different ways to reduce heat loss:
Simple ways to reduce heat loss include fitting carpets, curtains and draught excluders. It is even possible to fit reflective foil behind radiators.
Heat loss through windows can be reduced by using double glazing. These windows have dry, trapped air between two panes of glass. This reduces heat loss by conduction and convection. Air is a poor conductor and by trapping it between the panes, convection currents cannot be set up.
Heat loss through walls can be reduced using cavity wall insulation. This involves blowing insulating material into the gap between the brick and the inside wall. Insulating materials are bad conductors and so this reduces the heat loss by conduction. The material also prevents air circulating inside the cavity, therefore reducing heat loss by convection.
Heat loss through the roof can be reduced by laying loft insulation. Air is trapped between the fibres of the insulation, reducing heat loss by conduction.
How can heat transfers be reduced in the human body?
Heat energy is lost from the human body because body temperature is higher than room temperature.
However, there are ways that these losses can be reduced.
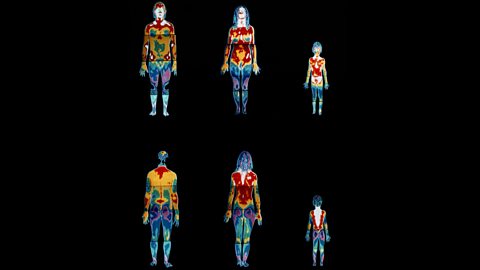
This is a thermogramImage made by detecting infrared radiation rather than visible light. Different colours are used to represent the different temperatures of the objects in the image. of a man, woman and child.
The white and red parts are the hottest and so are losing most heat.
Orange and green represent medium temperatures, and blue and purple are the coldest parts.
It is easy to see that the heads of all three people are the hottest parts, followed by their torsos.
Their arms and legs show medium temperatures, while their hands and feet are among the coldest parts.
It is in these places that we sometimes get frostbiteAn injury caused when skin and underlying tissue freeze as a result of extended exposure to very cold temperatures. It often affects the fingers, toes, nose, and ears. in very cold conditions.
Hair on our head reduces heat loss because air is trapped between individual hairs.
To reduce heat transfers from our bodies, we can wear insulating clothing - such as gloves, scarves, hats and thermal socks - in cold weather.
The more layers we wear, the more air can be trapped and the warmer we will remain.
Some clothes, such as wool, are excellent insulators, because they trap lots of air between individual fibres.
What are the everyday applications of heat transfer?
Vacuum flask
The vacuum flask is made from a glass bottle with two walls separated by a vacuumA volume of space that contains no matter. which prevents heat transfer by conductionThe transfer of heat through a material by transferring kinetic energy from one particle to another. and convectionThe transfer of heat energy through a moving liquid or gas. through the sides.
The glass walls are made of shiny silver to prevent heat transfer by heat radiationThis is when heat energy is transferred through electromagnetic waves generated by an object's temperature. Unlike conduction and convection, this type of heat transfer occurs even in the absence of a medium, such as in a vacuum..
The plastic screw top stopper usually contains cork or foam with trapped air to reduce heat loss by convection and conduction.
It can also be used to keep a cold drink cold, in this situation the heat is trying to enter the flask from the warmer outside region.
| Feature | Job |
|---|---|
| Vacuum between the two glass walls. | Prevents conduction and convection through the sides. |
| Silvered surfaces. | Minimises heat transfer by radiation. |
| Plastic cap. | Minimises conduction and convection through the top of the flask. |
| Outer plastic case and sponge/cork filling. | Protects the fragile glass bottle from becoming damaged by knocks and bumps. |
| Feature | Conduction | Convection | Radiation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum | \(\checkmark\) | \(\checkmark\) | \(\text{X}\) |
| Silvered surfaces | \(\text{X}\) | \(\text{X}\) | \(\checkmark\) |
| Plastic cap | \(\checkmark\) | \(\checkmark\) | \(\text{X}\) |
Refrigerator
A refrigerator works by transferring heat energy from inside the fridge to the room outside and therefore lowering the temperature on the inside of the fridge.
Heat energy inside the cabinet is absorbed by a coolant which circulates through pipes from inside to outside.
When the coolant passes through the pipes on the outside of the fridge it transfers this heat energy to the room.
The pipes on the back of the fridge containing the coolant are normally black, thin and have metal fins attached.
How much do you know about heat transfer?
More on Unit 1: Energy
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 5

- count2 of 5

- count3 of 5
