Exam practice
GCSE Physics: exam-style quiz by topic
Try this quiz based on GCSE Physics past papers. Choose the topic you would like to revise and answer the questions.
GCSE Physics: exam-style questions
Use our interactive tests to understand how the CCEA foundation and higher physics GCSE exams work. Revise topics such as forces and learn equations and formulae.
GCSE Physics: quick-fire questions
Free quiz to help you revise for your CCEA foundation and higher GCSE exams, based on GCSE physics past papers. Revise formulae, equations and more.

Quizzes
Quiz: Radioactive decay
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying stable nuclei, nuclear radiation, half life and nuclear equations.

Quiz: Models of the atom
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying developing the atom, Rutherford and the nucleus and further developments to the atomic model.
Quiz: Nuclear fission and fusion
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying nuclear fission, fission reactors and nuclear fusion.

Quiz: Atoms isotopes and ions
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying structure of the atom, atoms and isotopes and ions.

Quiz: The life cycle of a star
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying the formation and life cycle of stars, main sequence stars and supernovae.
Quiz: Density of materials
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying density, volume and investigating density.

Quiz: Scientific skills
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE physics students studying planning, observing, analysing, evaluating an experiment and scientific equipment.

Unit 1: Motion
Calculating motion - CCEA
What are scalar and vector quantities and how are they treated differently in calculations?

Velocity and acceleration – CCEA
What is the difference between velocity and acceleration? How are they calculated?

Distance-time graphs - CCEA
What are distance-time graphs and what do they show?
Speed-time graphs - CCEA
What do speed-time graphs show and how are they used to make calculations?
Unit 1: Forces
Force and Newton's laws - CCEA
What are Newton's three laws of motion? How do they describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it?

Mass and weight - CCEA
What do mass and weight mean in the world of physics? What is the difference between them?

Hooke's law - CCEA
What is Hooke's law? How is it investigated through practical work? What is the 'spring constant'?

Pressure - CCEA
What is pressure and how is it calculated? Why is it important in everyday situations?

Moment of a force
What are turning forces and where are they found in everyday life? What is the moment of a force and how is it investigated experimentally?

Unit 1: Density and kinetic theory
Density - CCEA
What is density and how is it used to make a fair comparison between materials?

Kinetic theory - CCEA
How does the kinetic particle theory explain the properties of solids, liquids and gases?

Interactive activity: States of matter - CCEA
Find out what happens when states of matter change with this interactive diagram designed to aid your understanding of the GCSE CCEA physics specification.

Unit 1: Energy
Energy forms - CCEA
How can energy be transferred or stored? What is the unit of measurement for energy? What does the Principle of Conservation of Energy state?

Energy resources - CCEA
What are the main types of energy? What are energy transfer diagrams and what do they show?

Work, power and efficiency - CCEA
What happens when work is done on an object and energy is transferred? What is the relationship between power and work done? What is efficiency a measure of?

Kinetic and gravitational potential energy - CCEA
What is kinetic and gravitational potential energy? How are they calculated?

Heat transfer - CCEA
What are the different types of heat transfer and how do they occur?

Unit 1: Atomic and nuclear physics
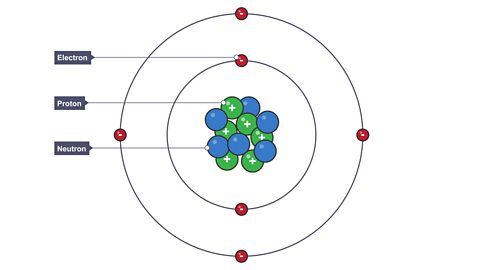
The structure of the atom - CCEA
What do atoms consist of? How were these different elements discovered?
The structure of the nucleus - CCEA
What is mass number and atomic number? What do they reveal about the nucleus of an atom?

Radioactive decay and half-life - CCEA
What is radioactive decay and how does it occur? What is the difference between alpha, beta and gamma radiation? What is half-life and how is it used in calculations?

The dangers and uses of radiation - CCEA
Why is radiation hazardous to humans? What is background radiation? How is radiation used in medicine, industry and agriculture?
Nuclear fission - CCEA
What type of energy is nuclear fission? How is it used to generate electricity in a nuclear power station? What are its advantages and disadvantages?
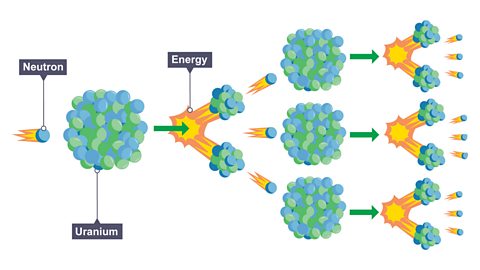
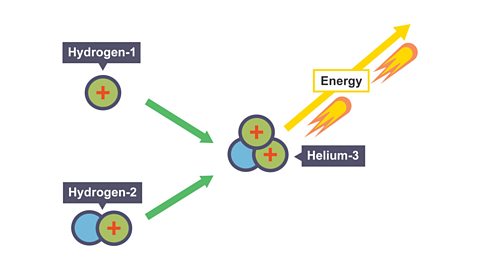
Nuclear fusion - CCEA
What is nuclear fusion and where does this occur? What are the arguments for and against developing fusion as an energy source?
Unit 2: Waves
Types of wave - CCEA
How do waves transfer energy from one place to another? What is the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?

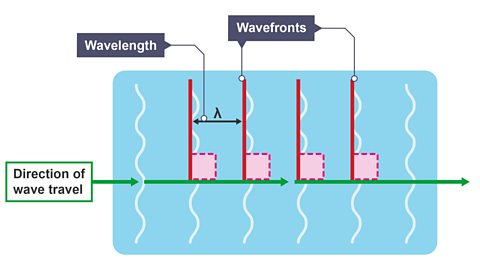
Wave features - CCEA
What are the key features of a wave? How is amplitude, wavelength and frequency measured?

Reflection and refraction of waves - CCEA
What does it mean when a wave reflects and refracts? How are these displayed in wave diagrams?
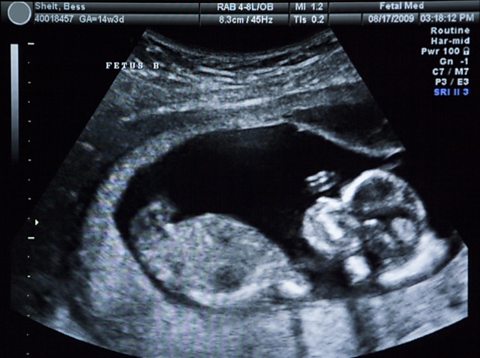
Echoes and sonar - CCEA
What are echoes and how are they used by sonar to map areas and locate objects? What is ultrasound and how is it used in medicine and industry?
Electromagnetic waves and radar - CCEA
What type of wave are electromagnetic waves? What are their properties and how are they used in everyday life?

Unit 2: Light
Reflection and refraction of light - CCEA
What are the laws of reflection and refraction? How can the refraction of light be investigated experimentally?
Critical angle and total internal reflection (Higher tier only) - CCEA
What is critical angle and total internal reflection? How can this be demonstrated experimentally? How is it used in communication technology and other aspects of everyday life?

Lenses - CCEA
What are the different types of lens and how are they used to correct human sight? What is focal length and how is it measured?

Unit 2: Electricity
Conductors and insulators - CCEA
What is electric current and how is it caused by moving electric charges? What are the effects of charge and electric fields on conductors and insulators?

Charge, current and voltage - CCEA
What is charge and how is it measured? How is current and voltage calculated?
Ohm’s law, electric power and energy - CCEA
What does Ohm's law state about resistance? What is the relationship between resistance and temperature?

Calculating resistance - CCEA
How is resistance calculated in series and parallel circuits? What is the relationship between resistance and the length of a conductor?

Electricity in the home - CCEA
What is the difference between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC? How is electricity used to power devices in homes?

Unit 2: Magnetism and electromagnetism
Magnetic fields - CCEA
What are magnets and electromagnets? How are magnetic fields detected? How is the strength of an electromagnetic investigated through practical work?

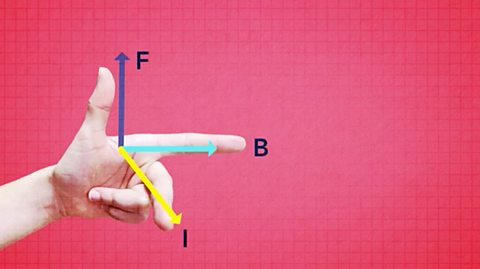
The motor effect - CCEA (Higher tier only)
How do magnetic fields interact to produce the motor effect? What is Fleming's left hand rule?
The AC generator - CCEA
What does the AC generator consist of and how does it work? How is it used in power stations in the large-scale generation of electricity for homes and industry?

The transformer – CCEA
What are the two types of transformer? What is their role in the flow of electricity to homes and businesses?

Unit 2: Space physics
The Solar System - CCEA
What does the Solar System consist of? What are artificial satellites and what do they do?
Stars - CCEA
How are stars formed and what is their lifecycle? What are supernovas and black holes?

The Universe - CCEA
How does the Big Bang theory explain how the Universe was formed and why it is still expanding? What evidence is there to support the Big Bang theory?

Space travel and life on other planets - CCEA
How has space exploration benefited many areas of science and technology? What are the risks involved in travelling to outer space and to other planets? What is a light year?

Unit 3 (a): Prescribed practicals
Prescribed practical P1: Motion down a ramp - CCEA
How the average speed of an object moving down a runway depends on the height of the runway.

Prescribed practical P2: Hooke's law - CCEA
How to carry out an experiment to investigate Hooke's law.

Prescribed practical P3: The principle of moments - CCEA
How to carry out an experiment to investigate the principle of moments.

Prescribed practical P4: Mass and volume - CCEA
How to carry out an experiment to investigate the relationship between the mass and volume of liquids and regular solids.

Prescribed practical P5: Measuring personal power - CCEA
How to plan and carry out an experiment to measure personal power.

Prescribed practical P6: Refraction of light
How to carry out prescribed practical P6 - the refraction of light.

Prescribed practical P7: Ohm's law - CCEA
How to safely plan and carry out an investigation into current, voltage, resistance and Ohm's law.

Prescribed practical P8: The resistance of a metallic conductor - CCEA
How to conduct an investigation into the resistance of a metallic conductor.

Prescribed practical P9: The strength of an electromagnet - CCEA
How to safely plan and carry out an investigation into the strength of a magnetic field.

Unit 3 (b): Practical skills
Practical skills (GCSE Physics) - CCEA
Everything CCEA students need to know about practical skills for GCSE Physics.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link